PROMOTING DENTAL HEALTH AT EVERY STAGE
We are specialized in Gum Disease Treatment.
Dental Gum Disease treatment focus on managing and reversing gum infections caused by the formation of plaque and bacteria. Gum disease also known as periodontal disease, gum disease ranges from mild gingivitis to severe tissues and bone damage. Gum disease timely intervention, can be effectively treated, Gum disease treatment prevent your oral health by further complications.
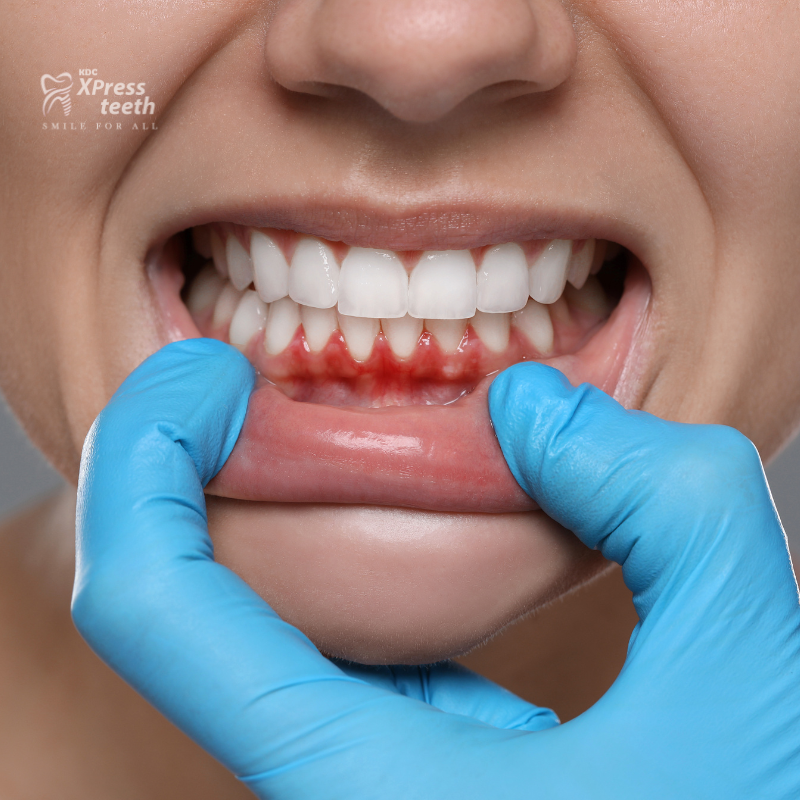
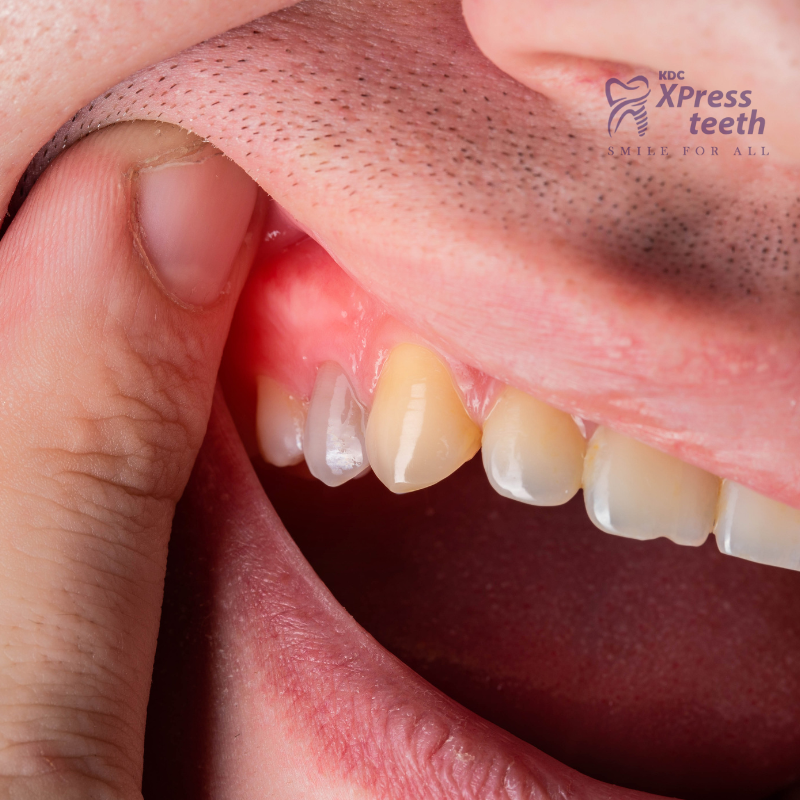
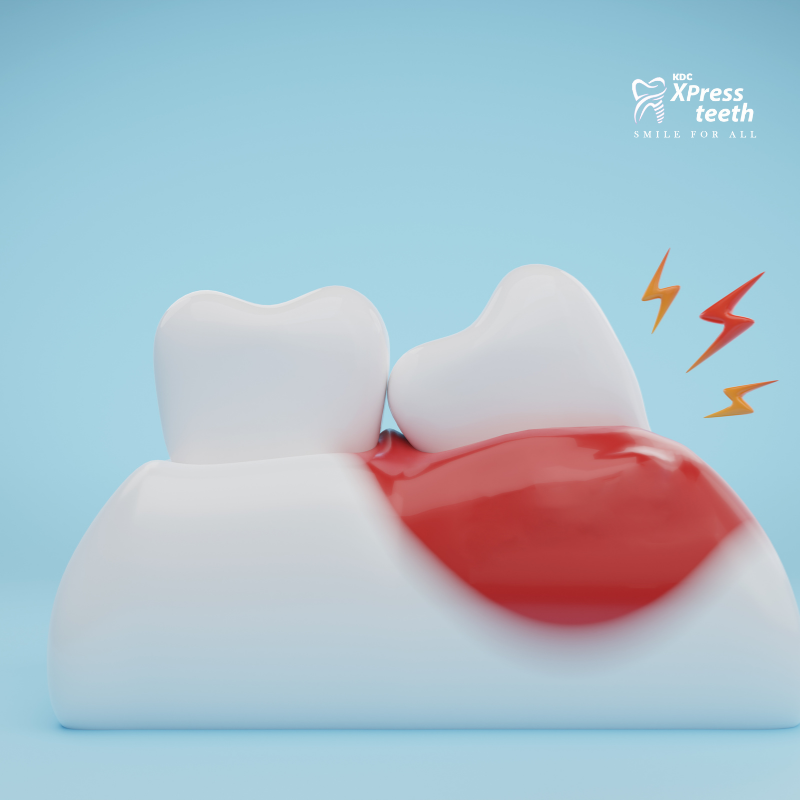
What is Gum Disease?
Gum disease occurs when bacteria in plaque cause inflammation of the gums, leading to redness, swelling, and bleeding. Left untreated, it can progress to periodontitis, where the gums pull away from the teeth, forming pockets that become infected and damage the supporting bone structure.
- Treatment Options for Gum Disease
- Professional Cleaning
- Removes plaque and tartar from above and below the gumline.
- Prevents the progression of gingivitis to periodontitis.
- Scaling and Root Planing (Deep Cleaning)
- A non-surgical procedure that cleans deep below the gumline to remove tartar and bacteria.
- Smooths the root surfaces to help gums reattach to teeth.
- Medications
- Antibiotics: Applied as gels or oral medications to eliminate infection.
- Antimicrobial Mouth Rinses: Used to reduce bacteria in the mouth.
- Surgical Treatments (For Advanced Gum Disease)
- Flap Surgery: Lifts gums to remove tartar and reduce pocket depth.
- Bone and Tissue Grafts: Regenerates lost bone and gum tissue.
- Guided Tissue Regeneration: Encourages bone growth in areas destroyed by periodontitis.
- Laser Therapy: Minimally invasive treatment to reduce bacteria and infected tissue.
Signs and Symptoms
- Red, swollen, or tender gums.
- Bleeding gums during brushing or flossing.
- Persistent bad breath or a bad taste in the mouth.
- Receding gums or teeth appearing longer.
- Loose or shifting teeth.
- Pain while chewing.
- Treatment Options for Gum Disease
- Professional Cleaning
- Removes plaque and tartar from above and below the gumline.
- Prevents the progression of gingivitis to periodontitis.
- Scaling and Root Planing (Deep Cleaning)
- A non-surgical procedure that cleans deep below the gumline to remove tartar and bacteria.
- Smooths the root surfaces to help gums reattach to teeth.
- Medications
- Antibiotics: Applied as gels or oral medications to eliminate infection.
- Antimicrobial Mouth Rinses: Used to reduce bacteria in the mouth.
- Surgical Treatments (For Advanced Gum Disease)
- Flap Surgery: Lifts gums to remove tartar and reduce pocket depth.
- Bone and Tissue Grafts: Regenerates lost bone and gum tissue.
- Guided Tissue Regeneration: Encourages bone growth in areas destroyed by periodontitis.
- Laser Therapy: Minimally invasive treatment to reduce bacteria and infected tissue.
- Prevention and Maintenance
- Practice Good Oral Hygiene: Brush twice daily and floss regularly to remove plaque.
- Regular Dental Checkups: Visit your dentist for professional cleanings and early detection.
- Healthy Lifestyle Choices: Quit smoking, eat a balanced diet, and manage stress to boost gum health.
- Control Systemic Conditions: Manage health conditions like diabetes that may contribute to gum disease.
- Benefits of Gum Disease Treatment
- Prevents tooth loss by preserving the supporting structures of your teeth.
- Reduces inflammation, pain, and discomfort.
- Improves overall oral and systemic health.
- Restores confidence in your smile and freshens breath.
Gum disease treatment is crucial to a maintain a healthy smile and preventing serious complications, so the gum disease treatment should be done at the earliest if you notice signs of gum disease immediately consult our dentists at KDC Xpress Teeth or periodontist for personalized treatment plan or procedure. A proactive approach looks after your long-lasting oral health and well-being.

